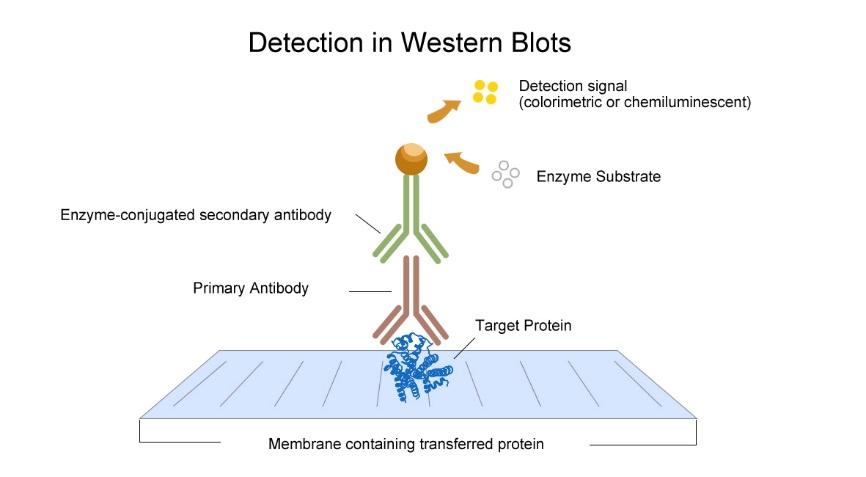
Western blotting, also known as protein immunoblotting, is a method used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide chains. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane, where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The antibodies are typically conjugated to an enzyme or radioactive molecule, allowing visualization of the protein bands and quantitation of protein levels in different samples.
Sample Preparation
The first step in Western Blotting is preparing the tissue or cell extract containing the proteins of interest. Common techniques include homogenizing or lysing the sample to release intracellular proteins. Protease and phosphatase inhibitors are often added to the extraction buffer to prevent degradation of proteins during preparation. The extract is then centrifuged to remove cell debris and organelles, leaving the supernatant containing soluble proteins. Total protein concentration is determined so equivalent amounts of protein can be loaded in each lane during electrophoresis.
Gel Electrophoresis
Extracted proteins are separated by gel electrophoresis based on their molecular weight. SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) is commonly used, where proteins are denatured and given a negative charge by binding to SDS detergent. An electric current is applied, causing proteins to migrate through the polyacrylamide gel matrix towards the positive electrode. Smaller proteins travel farther than larger proteins, resulting in separation by size. A molecular weight marker ladder is run alongside the samples as a reference.
Protein Transfer
After electrophoretic separation, proteins are transferred from the polyacrylamide gel to a nitrocellulose or PVDF membrane using a wet or semi-dry transfer apparatus. An electric current moves the proteins from the gel to the membrane while maintaining the molecular weight separation achieved during electrophoresis. The membrane is then blocked to prevent nonspecific binding during subsequent antibody incubation steps.
Get More Insights on- Western Blotting
Explore More Related Article On- Power Electronics Market
Get More Insights—Access the Report in the Language that Resonates with You: